Secure Hash Algorithm 512-bit (SHA-512)
Authentication Application and Python Source Code
Secure Hash Algorithm 512-bit (SHA-512) is a cryptographic hash function that produces a 512-bit (64-byte) hash value from data (file or folder) of any size.
DOWNLOADS
SHA-512.exe - Desktop Application
SHA-512.py - Python Source Code
Password: password
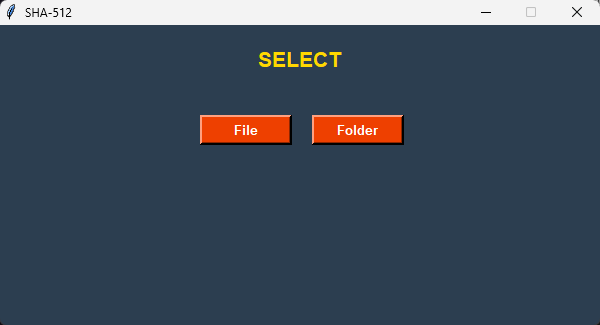
INSTRUCTIONS
Select “Next”
Select “File” or “Folder” and choose.
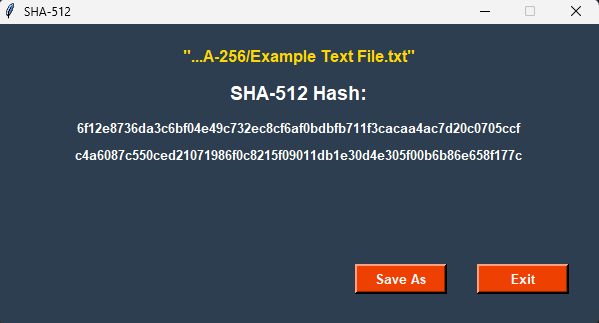
SHA-512 Hash of “File” or “Folder”
Select “Save As” or “Exit”
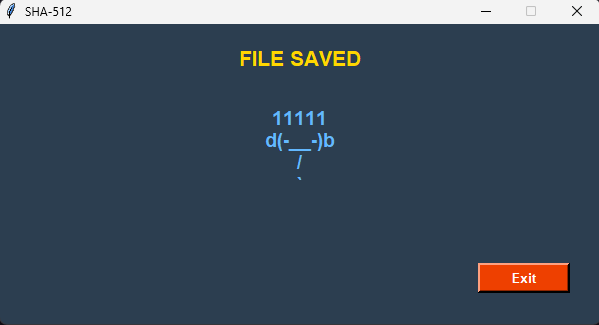
SHA-512 Hash File has been saved.
Select “Exit”
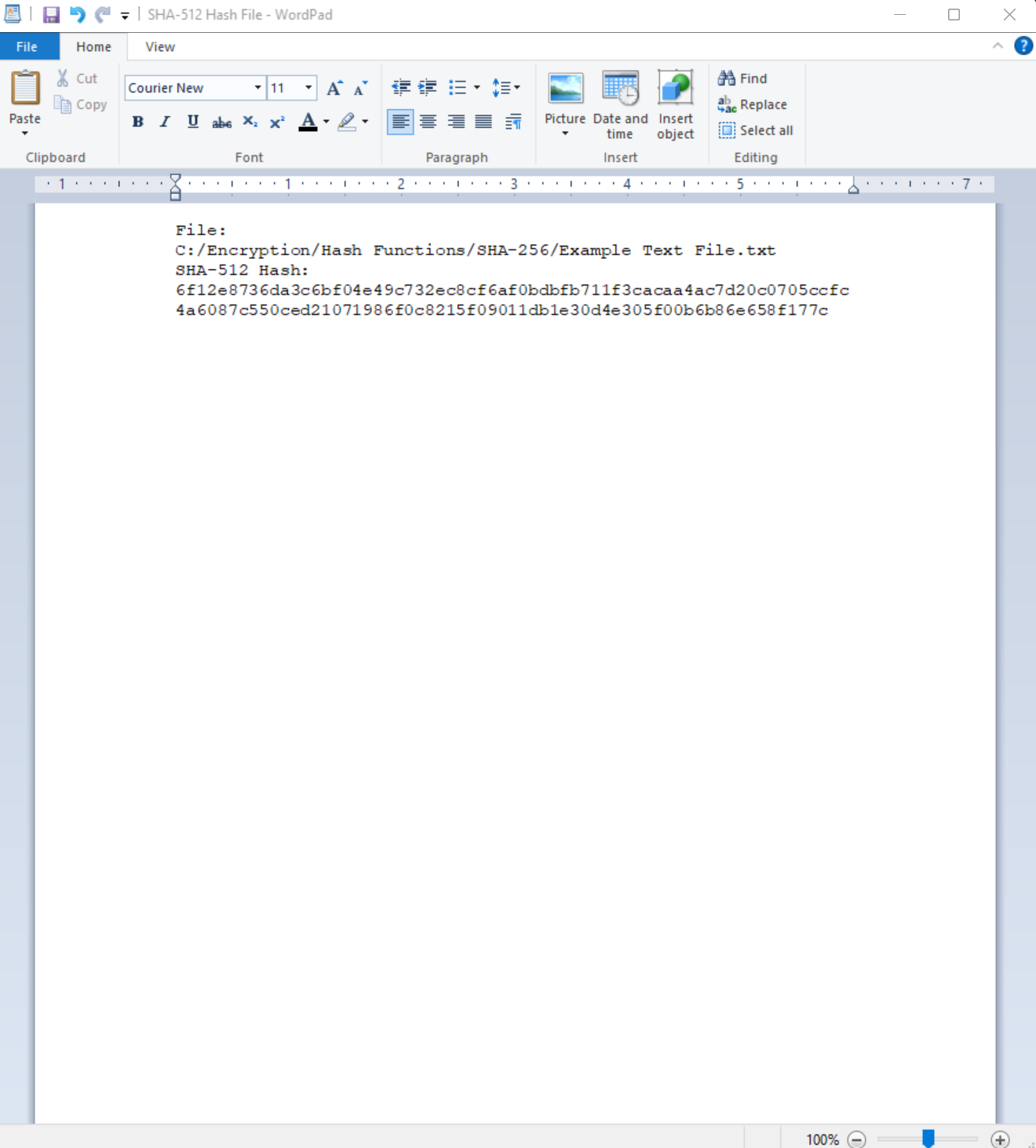
Saved SHA-512 Hash File
BACKGROUND
The Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) was developed by the National Security Agency (NSA) in the United States and published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) as a federal information processing standard. The SHA-2 family of hash functions was developed to address vulnerabilities found in earlier versions, such as SHA-0 and SHA-1.
SHA-512 is part of the SHA-2 family and operates on 1024-bit blocks, producing a 512-bit hash value. It offers a higher level of security and collision resistance compared to SHA-256 due to its larger output size and longer block size.
SHA-512, like SHA-256, iteratively processes input data in blocks and applies a series of logical operations, such as bitwise operations and modular addition, in its compression function. This function operates on each block of the message in sequence, with 80 rounds divided into four rounds of 20 operations each.
The resulting hash value is unique to the input data, making it virtually impossible to reverse-engineer the original input from the hash value. SHA-512 is widely used in various security applications, including digital signatures, SSL/TLS encryption, blockchain technology, and password hashing algorithms, where stronger cryptographic properties are required.
Its development and adoption have significantly enhanced the security of cryptographic systems and protocols, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of digital information in today's interconnected world.
HOW IT WORKS
Padding: The input message is padded to ensure its length is a multiple of 1024 bits. Padding involves appending a single '1' bit followed by a series of '0' bits, and then appending the length of the original message in binary to ensure the final block is a multiple of 1024 bits.
Breaking into Blocks: The padded message is divided into blocks of 1024 bits each.
Initializing Constants: SHA-512 uses a set of initial constants, similar to SHA-256, for its compression function.
Initializing Hash Values: SHA-512 initializes eight 64-bit variables (buffers) with the hash values obtained from the previous hash computation.
Compression Function: The compression function operates on each block of the message in sequence. It consists of 80 rounds, divided into four rounds of 20 operations each.
Message Schedule: Each 1024-bit block is expanded into a message schedule array of 80 64-bit words.
Round Constants: Round constants are used in each round to modify the state of the working variables.
Operations: Each round consists of various bitwise operations, such as AND, XOR, and NOT, along with modular addition and rotation operations, applied to the working variables and the message schedule.
Final Hash Calculation: After processing all blocks, the final hash value is computed by concatenating the final values of the working variables in hexadecimal format. This produces a 512-bit hash value unique to the input message.